NASA Shared an Image of Sand-Dunes Captured on Mars & It’s Stunning!
NASA shared a picture of sand-dunes that look like creepy earthworms are making their way across the red planet. Is it a snake or earthworm? Let’s find it out.

Once again NASA is in the headlines after the agency shared a picture of Mars ‘barchan dunes’. The dunes were captured near the Mars Nili Patera and were the result of wind constantly blowing in the same direction.
As wild as the worms crossing Arrakis, the erosive Martian surface reveals snaking sand dunes across the desert. With same wavelengths as a human, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's @HiRISE camera can spot objects as small as Alia Atreides. Look closer: https://t.co/Q6HaHlqSiT pic.twitter.com/jF9FZOCH2b
— NASA (@NASA) February 16, 2019
What is Barchan Dunes?
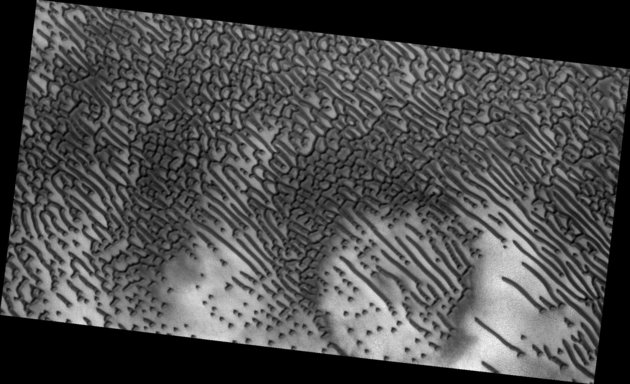
The term, Barchan dunes, was introduced by Alexander Von Middendorf for crescent-shaped dunes in inland desert regions. They are produced when wind constantly flows in one direction. Recently, Barchan dunes have been observed on the red planet where the atmosphere produced wind strong enough to move both sand and dust.
NASA Shared a 360-Degree View of Rock Hall
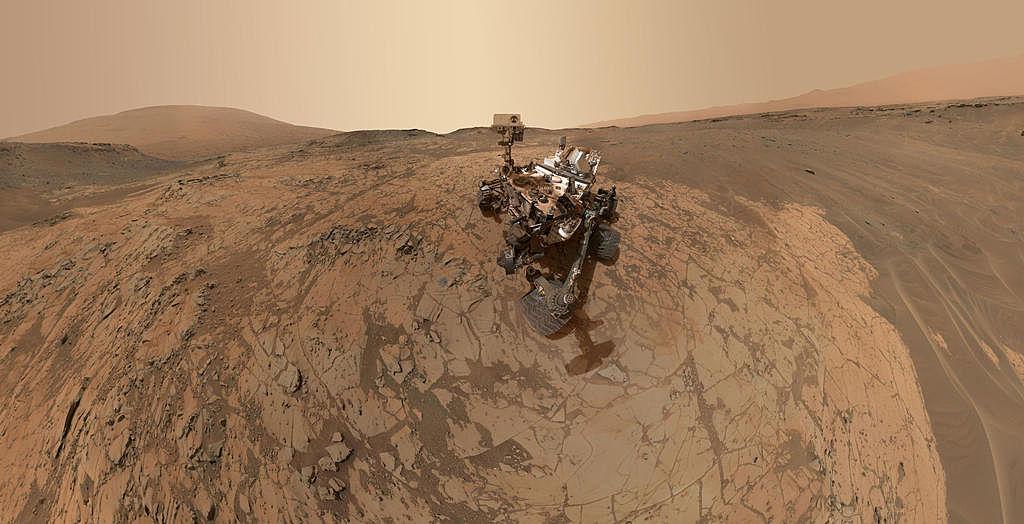
The agency revealed that the orientation of the dunes describes how they are formed. According to the High-Resolution Imaging Science Expert (HiRISE), Nili Patera is an area on Mars where dunes are moving rapidly. Meanwhile, NASA also posted a 360-degree view of Mars “Rock Hall” captured by the Mars Curiosity Rover. It shared the panorama video which was taken before the lander descended from Vera Rubin Ridge (a region of Mars, Mount sharp) that has been capturing and gathering data from over a year. (13.1)
Greetings from Mars, Earthlings! ???? Take a look at the Red Planet in 360º panorama video to see @MarsCuriosity’s view of an area named "Rock Hall” and the new region that the rover will spend the next year exploring: https://t.co/UvJCqfSHF6 pic.twitter.com/b5rX8z6ZpD
— NASA (@NASA) February 10, 2019
The video taken on 19th December showed the area depicting its last hole at Rock Hall and the region (clay-bearing unit) it will be exploring in the coming year. The Curiosity has been searching for Vera Rubin Ridge since 2007. The rover has moved towards the clay-bearing unit which is now known as “Glen Torridon.”
Scientists are exploring the ancient lakes that helped in gathering data from clay minerals in the unit.
Curiosity Project Scientist Ashwin Vasavada of JPL said –
“In addition to indicating a previously wet environment, clay minerals are known to trap and preserve organic molecules.”
He further added –
"That makes this area especially promising, and the team is already surveying the area for its next drill site.”
The Pictures Shared Also Highlight the Light-Toned Layers of Deposits on Red Planet

The picture captured by HiRISE highlights the light-toned layers of sedimentary rocks on red planet surface which were the result of erosion. The sand-dunes on the rocks are the new geological features.
The team also posted an image of Martian “barchan dunes.” The barchan dunes are identified by their long and extended crescent form and were formed due to the wind blowing in the same direction. The slow movement of sand is what causes them to move over time.
Sand dunes...on Mars! ???? With an elongated crescent form, these "barchan dunes" are located near Nili Patera and are formed by the continuous action of the wind blowing in the same direction. Take a closer look: https://t.co/5pvxhqgbuL pic.twitter.com/HutyvjFQGa
— NASA (@NASA) February 10, 2019
The barchans dunes were formed by wind blowing from east to west which then moves to sand grains towards the top. This movement creates ripples on the slope. Nili Patera is a field on Mars planet and is located on top of a lava bed where a volcano Nili Patera caldera of Syrtis Major used to be.
In 2018, NASA reported that just to the south of the group of barchans dunes is one large dune that appeared like turquoise blue but has a different composition than the surrounding.
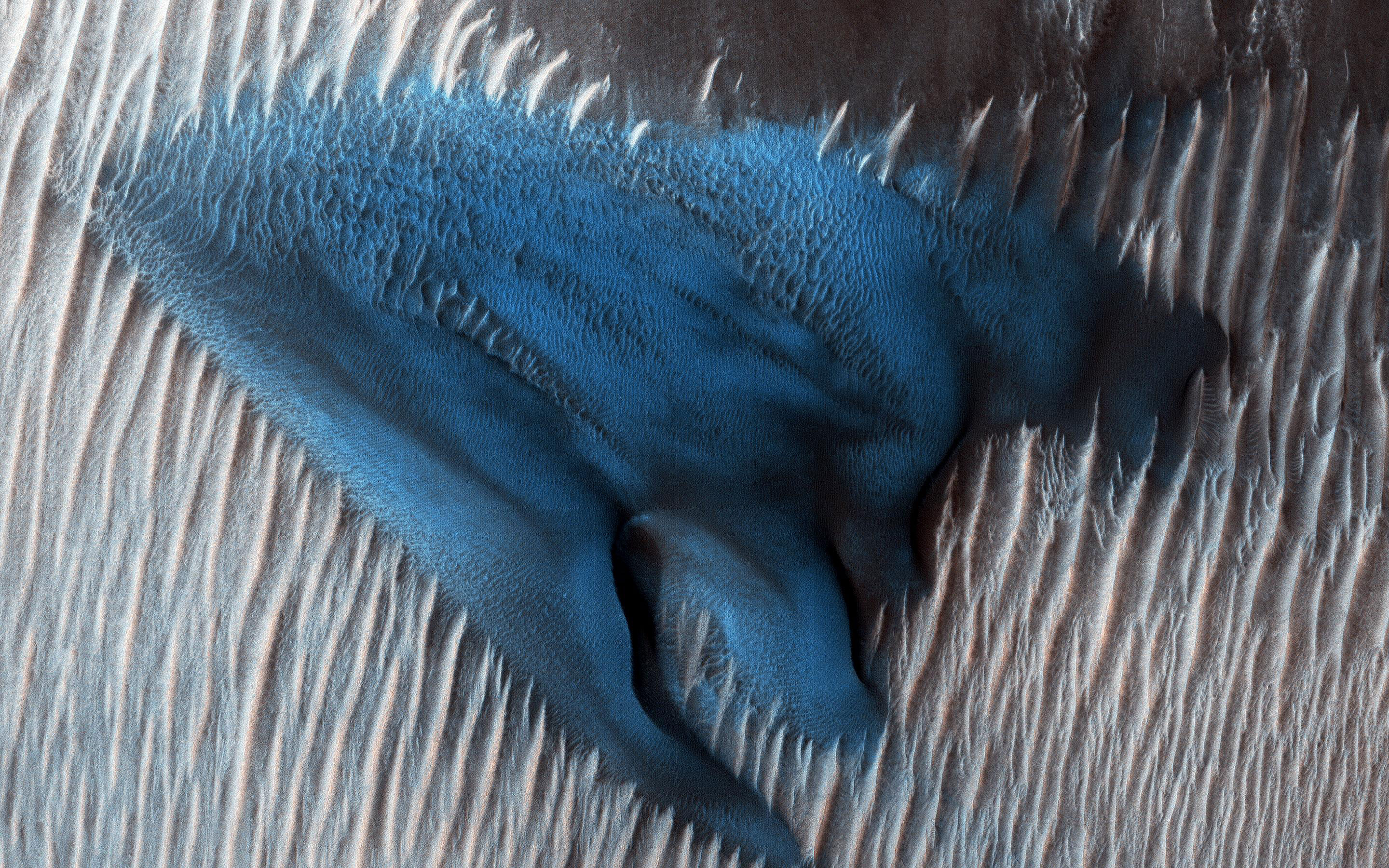

The dune image was taken by the MRO (Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) and located in the Mars Lyot Crater, a large crater on the planet better known for its patterned ground.
McEwen, the Director of the Planetary Image Research Laboratory, said –
“The images are given min-max stretches in each individual color image to increase contrast. The dunes are actually grey, but appear relatively blue after such a stretch because most of Mars is red.”
Though, it is more grayish than blue but appears blue in an enhanced color image taken by MRO. This is what the researchers do to see the image clearly. The MRO which went into space in 2005 is studying the history of water on Mars.
The red planet has always attracted the researchers for different reasons. Earlier it was revealed that aliens have an existence on Mars. But we are still figuring if it is true or not.
And now it is sand-dunes captured on Mars. The pictures of sand-dunes are interesting, and we are hoping that the scientists will explore it a bit more and would come up with new details about Mars.
Concluding Thoughts
Do you know Mars can be our new home? Well, there is no evidence found, but some pieces of evidence suggest that during the Noachian period, it had water and have been habitable for microorganisms. Here are more reasons why Mars can be considered as the potential planet where human habitation might happen.
Recently, US President Donald Trump also announced to offer unlimited funding to NASA to get humans to Mars by 2020. The planet Mars share major similarities to Earth. It has seasons like earth but, they last twice as long as in comparison to the earth.
Coming back to the recent discovery, the picture of sand-dunes on the Mars planet is compared to creepy worms. What do you think the picture shared resembles with- a snake or earthworms?
Popular Posts
What Is Trypophobia – A Disgust More Than Fear
"I can't really face small, irregularly or asymmetrically placed holes, they make me like, throw up in my mouth, cry a little bi...
Chandan Roy
16 Interesting Facts About Ambidextrous People
A lefty or left-handed uses his left hand more naturally and dominantly than the right hand. And the righty or right-handed is o...
Ethan Stephans
20 Interesting Facts About Meteoroid, Meteor and Meteorite
Watching celestial objects is a true delight. It is still fun to catch a sight of shooting stars when we grow up. A second of th...
Swati Bhandari








