10 Scientific Facts About Neurotransmitters that you Might Not Know
Neurotransmitters also referred as chemical messengers, assist the brain in managing the tissues and functions of the body through muscles and organs.
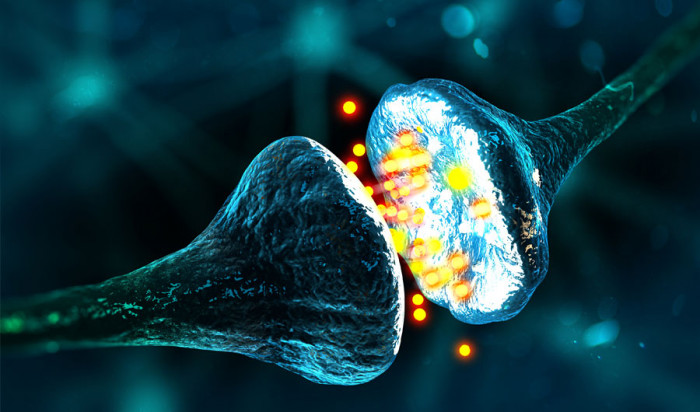
What do you understand by the term neurotransmitters? Neurotransmitters are a kind of brain chemical messengers that help or assist the brain in managing the functions of the body, organs, muscles, and tissues. It facilitates the communication of nerve impulses from one neuron to another body cell or neurons. Very few of people know that there are different types of neurotransmitters which are responsible for different functions.
Many neurotransmitters in the body are synthesized from plentiful precursors likely to be amino acids which are available from the diet and require only a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. The exact number of these brain messengers not known but it is studied that there are more than 100 neurotransmitters have been identified in the body.
1. There are Some Criteria to Identify Neurotransmitters

Not one but there are more than 100 types of chemical messengers in the body, but how you will identify them. The fact about neurotransmitters which is not known is it requires 4 main criteria to identify them.
• Chemical must be released and give some response in target if a neuron is active.
• The exact response should be obtained when a chemical is placed on the target.the
• The chemical must be treated synthetically in the neuron or otherwise present in it.
• A mechanism should exist for removing the chemical from the site after the work is done. (14.1)
2. The Size of Neurotransmitters May Vary
As there is the number of neurotransmitters, it is logical to say they also vary in size. Some of these chemical messengers are equal in the size of proteins while some come equals in the size of single amino acid. Large proteins usually size around 10nm, this means that normally neurotransmitters would size around 0.5 to 5 nanometers.
3. Glutamate is the Most Abundant Neurotransmitter Found
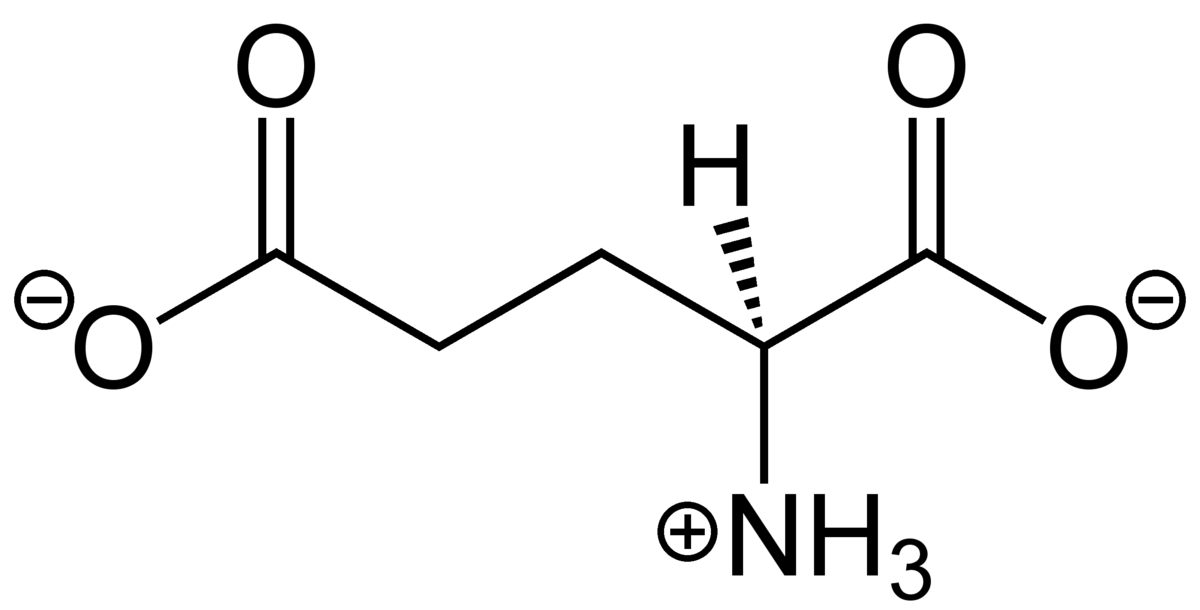

Sometimes these chemical messengers are classified into inhibitory and excitatory. The classification is usually based on the actions of neurons. Inhibitory neurotransmitters are recognized for producing a calming effect on the brain on the other hand excitatory neurotransmitters are those who excite the neurons.
Neurotransmitters are further categorized into peptides, monoamines, amino acids, purines, trace amines and others, with amino acids and peptides are major types. Over 50 peptides have been found and new are identified regularly. In many cases, a peptide is a major transmitter at a synapse. But the most transmitters widespread are glutamate which is over 90% of the synapse in the brain. It is used by every excitatory function in the brain and also serves as the prominent neurotransmitter for brain regions.
4. First Neurotransmitter Ever Discovered
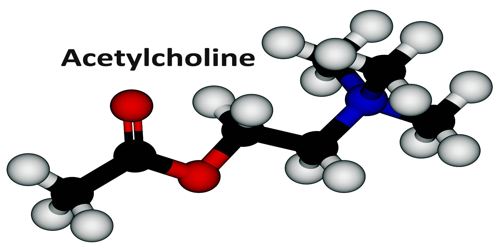
The first neurotransmitter to be discovered is Acetylcholine. It was discovered by Otto, Loewi. It is a kind of neurotransmitter which is mainly responsible for activating muscles. It causes our skeletal muscles to regulate and contract the endocrine system. The first ever discovered neurotransmitter also regulates the activities happening in the brain, which is related to learning and memory. In CNS acetylcholine inhibits the operation of a cholinergic system. A person suffering from Alzheimer’s disease is usually found to have the low level of acetylcholine.
It functions in both peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS).
5. Dopamine
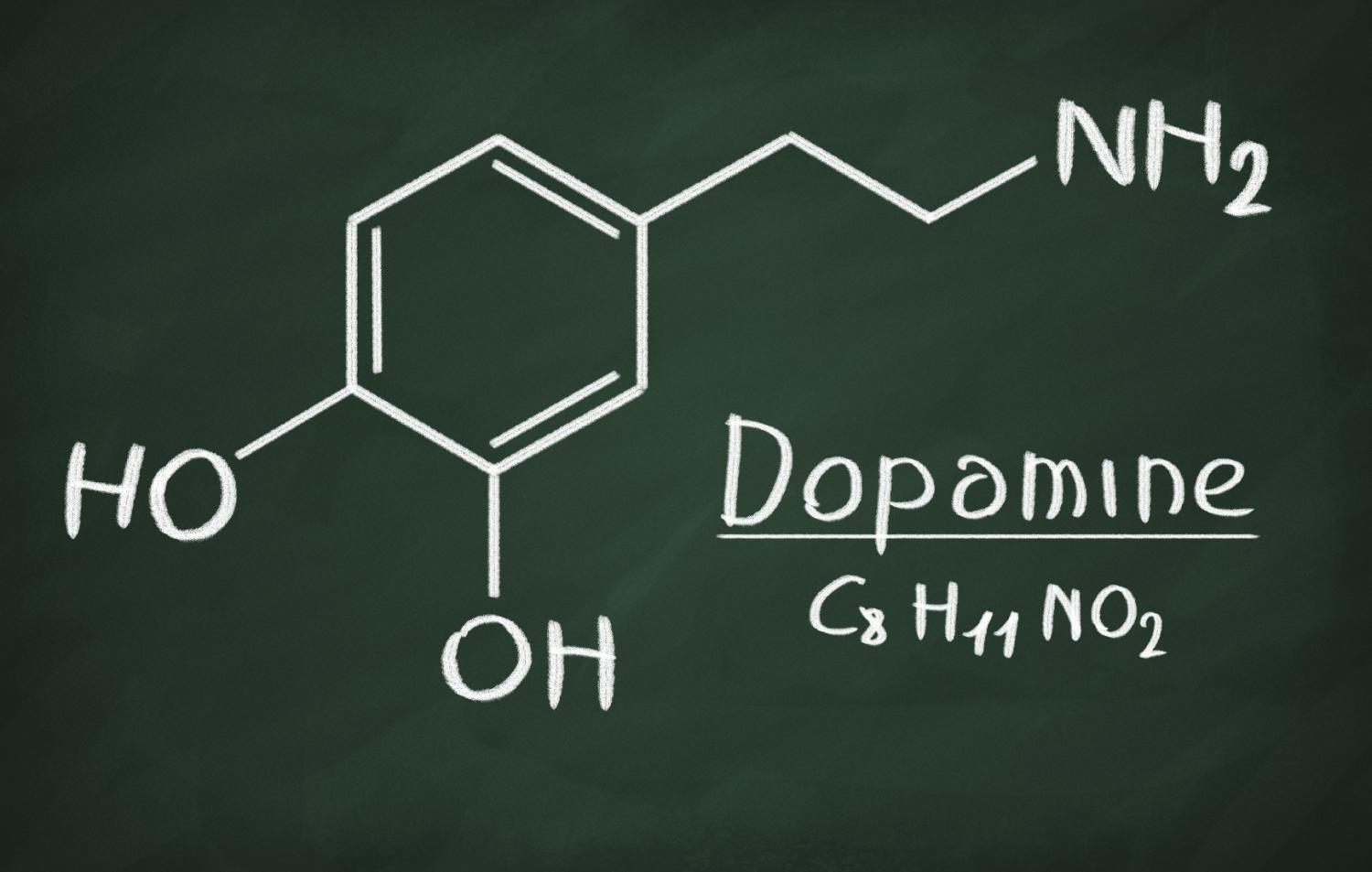
Dopamine is another major neurotransmitter responsible for monitoring the memory and motor control. It is a kind of chemical of phenethylamine and catecholamine families and plays a crucial role in supporting the brain. The lesser known scientific fact about dopamine Neurotransmitter is low or high levels of this chemical can result in memory issues - forgetting the immediately said, forgetting the items placed or not being able to stay focused.
When the level of dopamine is elevated it may result in hyperactivity and anxiety. It may further experience mood swings, attention disorders, autism etc. Dopamine injections are used to recover the conditions occurred when you are in shock or the conditions which are caused by surgery, trauma or kidney failure. (14.2)
6. Norepinephrine
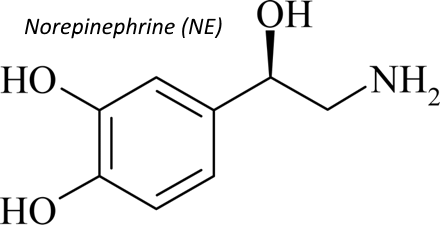
It is an excitatory chemical messenger that is majorly responsible for processes of focus and attention. It is also known as the stress hormone. Norepinephrine is produced by the adrenal medulla. The release of this chemical is lowest when falling asleep, it rises during wakefulness and reaches higher her level in the situations of danger or stress. In the brain it increases anxiety; it also increases blood pressure and promotes vigilance.
It is also called noradrenaline, a substance that is released from the ends of nerve fibers and increasing the force of skeletal muscle contraction and contraction of the heart. Norepinephrine is produced in nuclei yet delivers powerful effect on brain areas. Some of the side effects of Norepinephrine are the weakness, making the eyes more moist, increase in glucose uptake, cold feeling, irritation, skin changes and balance difficulties.
7. GABA
GABA is a kind of inhibitory neurotransmitter; it is a significant neurotransmitter that aids the conversion of messages between nervous system and brain. The main function of GABA is to reduce excitability, improve sleep and decrease inflammation. High levels of GABA may result in calming action that contributes energy and foggy thinking. The lesser known scientific fact about GABA is it is produced in the brain from glutamate. Its main function is to reduce the operation of nerve cells in the nervous system.
In addition, a deficiency of hormone can lead to symptoms like puberty and slow growth, GABA helps in increasing the levels of growth hormone, it also lowers the risk of heart disease and makes bone stronger. (14.3)
8. Epinephrine
Epinephrine is another excitatory neurotransmitter that regulates metabolism and blood pressure. It functions primarily to raise glucose levels in the blood. The extra amount of glucose in the body can then further be used, as a fuel during stress or exertion. It involves in controlling the body’s metallic response and making it prepare for the action while reducing or suppressing the non-emergency bodily processes. High levels of Epinephrine results in sleep issues, low adrenal function, depression, dizziness, burnout and chronic stress.
As a medication, this neurotransmitter is used to cure cardiac arrest, superficial bleeding, and anaphylaxis. It is usually produced by certain neurons and adrenal glands. It may have certain adverse effects like a headache, acute pulmonary edema, and tremor. This medication is also used in cases of emergencies to cure reactions like insect bites, or other substances.
9. Glutamate
Glutamate is a chemical that is used by nerve cells to send signals to other cells. It is considered as the major mediatory of the signals in CNS and is equally involved in the brain functioning including memory, cognition, and learning. It is considered as the primary neurotransmitter, for brain regions such as cerebellum granule cells.
Glutamate plays the crucial role in the improvement of growth cones and synaptogenesis during brain development. Elevated levels of Glutamate can hint about excitotoxicity. High levels are often linked with impulsivity, depression, anxiety, mental diseases and panic attacks. On the other side, Glutamate helps the brain function; it sends signals to the brain and plays a vital role in the brain development. The presence of glutamate might also signal our body about high protein foods. It also delivers great effect on cancer, and autoimmune pathological T cells. Glutamate slows down aging and increases lifespan. It also aids the treatment of bone diseases like osteoporosis. (14.4)
10. Glycine
Glycine consists of amino group and the acidic group which is attached to a carbon atom. When glycine is released into a synapse (a place where neurons transmit signals to each other) it binds to a receptor making the postsynaptic membrane more permeable to Cl-ion. It is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which gets deactivated in the synapse by the process of reabsorption by active transport back into the presynaptic membrane.
It is present in the brain stem and spinal cord and participates in sensor and motor functions. Glycine act as a building block for protein. It is colorless and sweet flavored crystalline solid. USP glycine has the number of uses, it is also used as an additive in animal feed, foods and pharmaceuticals and pet food. It also serves as a buffering agent in antiperspirants, toiletries, and cosmetics. Glycine is used for curing metabolic syndrome, sleep problems, schizophrenia, and stroke.
Popular Posts
What Is Trypophobia – A Disgust More Than Fear
"I can't really face small, irregularly or asymmetrically placed holes, they make me like, throw up in my mouth, cry a little bi...
Chandan Roy
16 Interesting Facts About Ambidextrous People
A lefty or left-handed uses his left hand more naturally and dominantly than the right hand. And the righty or right-handed is o...
Ethan Stephans
20 Interesting Facts About Meteoroid, Meteor and Meteorite
Watching celestial objects is a true delight. It is still fun to catch a sight of shooting stars when we grow up. A second of th...
Swati Bhandari








