The What, Why & How of Leukemia (Blood Cancer)
The cure for leukemia is completely based on age and other factors. Find out the most common diagnostic options and signs for leukemia here.
.jpg)
Cancer! Do you know there are more than 100 types of cancers identified? Cancer is a common name given to a collection of diseases. Changes in lifestyle, continuous work schedule, environmental changes, and more have led to an increase in the number of diseases. According to a study, 5 out of 8 people are diagnosed with cancer.
Many cancers can be controlled by maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, not eating too much red meat, and eating whole grains and fruits. However, there are certain cancers that cannot be prevented and cause the death of a person.
In all types of cancer, the body’s cell begins to divide and spread into tissues. Diseases like cancer can start anywhere in the human body. When cells damage or grow old, new cells take their place. But in cancer, this process functions differently. As cells become abnormal, old cells survive when they should die, and new cells are formed when they are not needed. These cells then divide and form ‘tumors.’
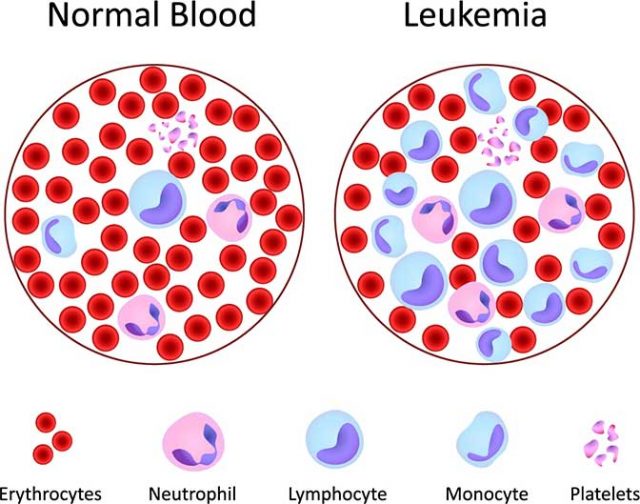
Most of the cancers form solid tumors, but cancer of the blood like leukemia does not form solid tumors. It is the cancer of the blood-forming tissue and includes the lymphatic system. Let us know more about this severe disease leukemia, its types, and symptoms below.
What is Leukemia?
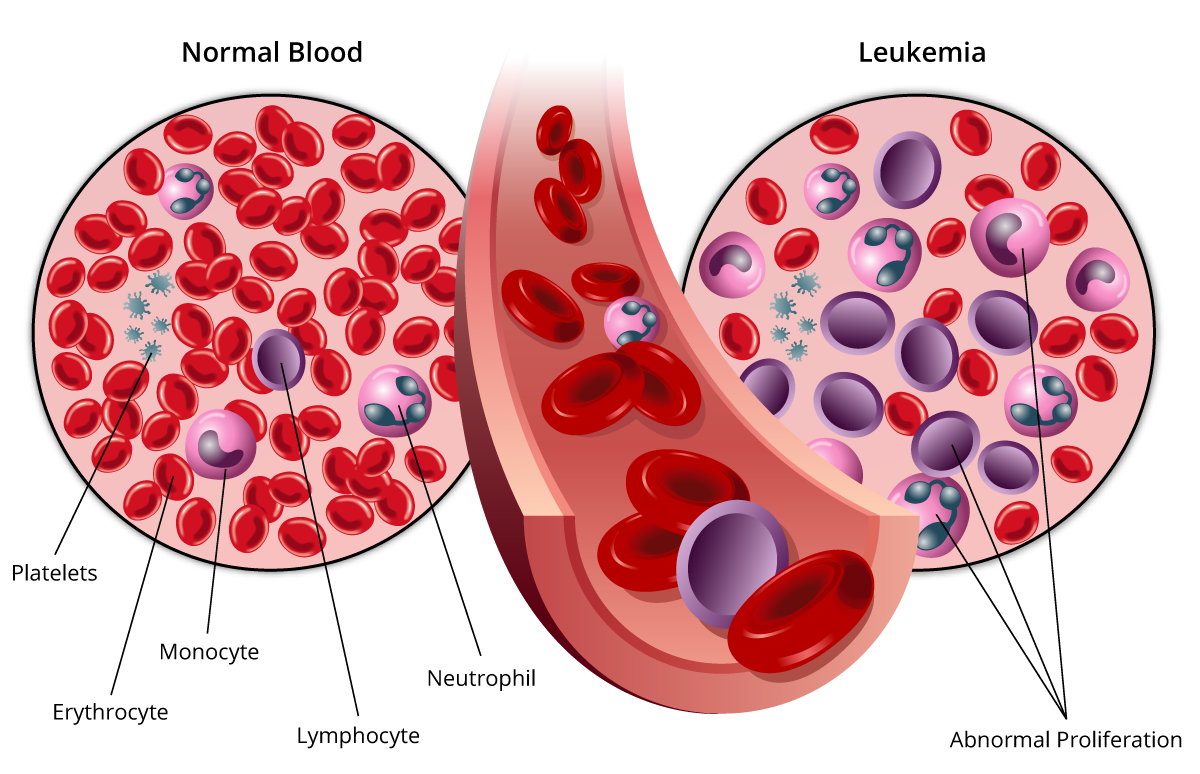
Leukemia is a group of cancers that begin in the bone marrow and affect the white blood cells. The exact cause of leukemia is not known; however, it is said that it happens when there is a problem with the production of blood cells. It usually involves white blood cells.
It is a different type of cancer that starts from the lungs, breast, or colon and then spreads to the bones. Do you know your white blood cells are the strongest infection fighters? They grow and divide in numbers according to your body requirements. Sometimes these white blood cells don’t develop fully and form leukemia cells. When the body forms leukemic cells, it no longer behaves normally and grows out of control. A person having leukemia has abnormal blood cells (white), which don’t function properly.
According to a study, in 2015, leukemia was present in over 2 million people and caused 400,000 deaths. It is the most common type of cancer in children. However, 80% of leukemia cases are diagnosed in adults with CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia), and AML (Acute Myeloid Leukemia) being the most common in adults. The treatment of leukemia may involve a combination of a bone marrow transplant, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. But the successful leukemia treatment depends on the type of leukemia and the age of a person.
Classification of Leukemia
Leukemia is divided into a variety of groups. The two general types of leukemia include –
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
It is characterized by an increase in the number of immature lymphocytes. This rapid increase makes the bone marrow unable to produce healthy blood cells. The symptoms of Acute Leukemia may include pale skin, bone pain, enlarged lymph nodes, blurry vision, dizziness, bruising, and fever. ALL is first treated with chemotherapy; if additional treatment is required, it involves radiation therapy and stem cell transplantation. It develops quickly and aggravates rapidly.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
CLL is characterized by relatively mature but still abnormal white blood cells. It is the most common cancer in older people but can also occur in any age group. The cells in Chronic Leukemia look normal but, they don’t fight infection as normally as WBC does. There are two types of CLL diagnosed in a person. The signs of Chronic Leukemia may include weight loss, fever, and weight loss.
The first type of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia grows very slowly. It is not a serious disease and takes a long time before the patient needs treatment. The second type of CLL grows at an extremely fast rate and is a more serious disease.
How is Bone Cancer Different from Leukemia?
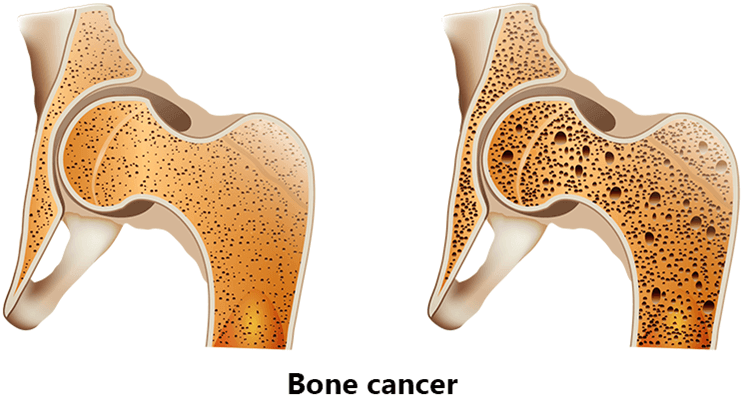
If anyone thinks of cancer and blood disorders, they think of a shortened lifespan. The same is the case with leukemia and other incurable cancers. Cancer can affect every human body part from head to toe. Both blood disease and cancer need special medical interventions and advanced treatment to be cured.
Bone cancer, as the name implies, occurs in the bones. It is the most painful type of cancer as it involves the bones. Bone cancer arises due to the infectious tumor that spreads in the bone tissue. Examples of bone cancer include fibrosarcoma and osteosarcoma. While removal of the part (amputation) can be the option, it cannot destroy or remove the cancer cells if they spread across the organs and other bones.
Leukemia is a specific type of blood cancer. It is identified by throw bone marrow aspiration biopsy. This kind of disease affects the WBCs. A person having leukemia is the most prone to infections. Treatment of leukemia is difficult. But it is said, the earlier it is diagnosed, the better it can be controlled. Leukemia is usually treated through bone marrow transplantation or chemotherapy.
What Causes Leukemia?
Well, there is no single known cause for different types of leukemia. But several risk factors may increase the chance of getting leukemia. It may include environmental and lifestyle factors. Among adults, the known cause of leukemia is associated with exposure to some hair dyes or petrochemicals. The specific risk factors may include-
- Family history
- Genetic disorders such as Down Syndrome
- Exposure to high levels of radiation
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Abnormality on chromosome 22
- Exposure to tobacco, gasoline, or chemical production facilities
Key Signs of Leukemia

Leukemia symptoms at first are very subtle and include headaches, unintentional weight loss, infections, and unexplained fever. Leukemia cannot be identified based only on symptoms; a keen awareness of other related diseases can also suggest when treatment is required. So here are some important signs to identify blood cancer.
Frequent Signs to Identify Blood Cancer
- Excessive Tiredness
Excessive tiredness is one of the most common symptoms of leukemia. The sign associated with leukemia interferes with daily activities and doesn’t improve with good sleep.
- WBCs Unable to Fight with Normal Infections
Cancerous WBCs can’t help fighting with a normal infection. As a result, a person having leukemia develops infection easily. Common sites of infection include the bladder, lungs, or throat.
- Abnormality of Enlarged Lymph Node
Sometimes leukemia cells in the lymph node can cause them to become swollen. A person with leukemia can feel an abnormality of the enlarged lymph node in the groin, neck, or armpit.
- Night Sweat
Night sweat is another common symptom of leukemia. Unlike the common signs related to menopause, night sweat associated with leukemia is different. It is described as ‘drenching’ which soaks through cloth and mattress below.
- Excessive Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss is another common symptom of leukemia and all other cancers. Unplanned weight loss can be defined as the loss of 5-6% or more body weight in 7-8 months.
- Excessive Bleeding
Although bleeding is common when the blood platelet count is low, excessive bleeding in some parts of the body can be serious.
i) Bleeding in the brain can cause rapid unconsciousness
ii) Bleeding in the intestine is a serious sign of cancer. It also rapidly drops blood pressure.
iii) Bleeding in the lungs may cause shortness of breath.
Multiple Myeloma - A Blood Cancer Linked to Leukemia and Lymphoma
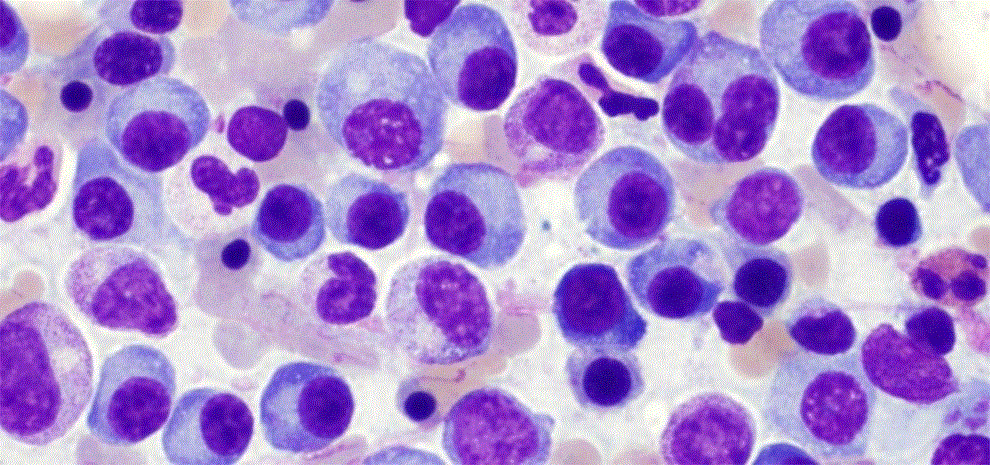
The Greek word ‘Myeloma’ means, marrow tumor (myelo – marrow and oma means tumor). Multiple Myeloma or better known as plasma cell myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells. The major source for the cause of multiple myeloma is unknown; however, in advanced anemia, bleeding and bone pain may occur. The risk factors for multiple myeloma include family history, radiation exposure, and certain harmful chemicals.
You might be aware that the immune system is made up of cells that work together and fights infections. Lymph cells are one of the important types of white blood cells that include B cells and T cells. When B cells respond to any disease or infection, they change into plasma cells. Further, these cells help the body in killing germs.
But when these plasma cells become cancerous and grow out of control, it is called multiple myeloma. It is somewhat related to leukemia and lymphoma. It is treatable but not incurable. When plasma cells release too much immunoglobulin into your blood and bones, they cause organ damage. As it gets even worse, the cells spill out of your bone marrow and cover all the body parts, which can cause more organ damage.
Cure for Leukemia
Treatment for Leukemia depends primarily on health, age, and the type of leukemia you have. Common treatments used to fight against leukemia are-
1. Chemotherapy
It is one of the most common and major treatments for leukemia. Chemotherapy uses chemicals to kill leukemia cells. Depending on their age and health, a person receives a dosage of drugs. The drugs used can be injected into a vein or taken in pill form.
2. Targeted Therapy
As the name implies, targeted therapy drugs attack particular parts of cancer cells. It is used when chemotherapy doesn’t work. For instance, Gleevec stops the reach of protein within the cells with chronic myelogenous leukemia.
3. Radiation Therapy
In leukemia, radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy leukemia cells and ultimately stops the growth. During this treatment, a person lies on the table, while a large machine directs the radiation to the point on a body.
A person may receive radiation only at one point, where there is a collection of leukemia cells or over the whole body.
4. Stem Cell Transplant
It is majorly used to restore healthy bone marrow in a person with leukemia. SCT or bone marrow transplant replaces the damaged bone marrow with healthy bone marrow. Before SCT, a patient receives radiation of therapy to destroy the unhealthy bones. A person with leukemia may receive stem cells from a donor (in case). It is very similar to a bone marrow transplant.
When to See a Doctor?
Be serious! Consult a doctor if you see any of the blood cancer symptoms described above. Though Leukemia symptoms are not specific, they could help you out in identifying other diseases as well (in case). Symptoms like drenching, night sweats, and severe headaches should be addressed without delay.
Although lymphatic symptoms are not identified at an early stage, consulting a physician and blood test is also an important step. (7.1)
How to Take Care When You Have Leukemia?
With time and family support, you can always fight leukemia. Below are the ways you can use to cope with this severe disease.
- Find a Good Listener – Find someone who is there to hear you out. Ask your doctor about the cancer organization or leukemia and lymphoma society to help you out in dealing with this disease.
- Learn More About Leukemia – Learn as much as you could about Leukemia. As you know more about leukemia, you become confident in making decisions.
Concluding Thoughts
There are several categories of blood cells that involve platelets, RBCs, and WBCs. Leukemia is referred to as the cancer of the White Blood Cells. It can be fatal, but with proper treatments and early diagnosis, it can be prevented and managed.
Although the successful treatment of leukemia is hard, with the enhancement in technology and research, one day, doctors might find an absolute cure for this disease.
Popular Posts
10 Amazing Lessons You Should Learn From Mr Olympia Jeremy Buendia
Jeremy Buendia is an fitness inspiration for people from all over the world, there is a reason why he has been so successful at what he has been doing. Don’t look for the reasons take some lessons from the fitness sensation right here, that can change your lives.
Ethan Stephans
Why Are Pubic Hair Thicker Than Body Hair?
As children we always had several questions about our bodies, which were alien to us, this post is to serve a decade-long curiosity of young boys/girls about their pubic hair and its texture.
Augustus Perez
7 Sleeping Tips That Every Woman Should Follow During Pregnancy
Pregnancy is not easy. Pregnant women experience a lot of changes in their bodies, like increased stomach size, frequent urination, and sleeping discomfort.
Still Unfold